Liver biopsy is a safe and quick procedure to help diagnose a liver problem, including its cause and severity. 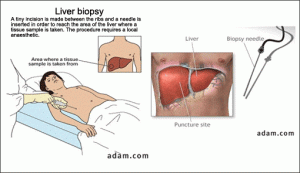
How is a Liver biopsy performed?
A liver biopsy is a procedure to remove a small piece of the liver so it can be examined with a microscope for signs of damage or disease. The three main types of liver biopsy are percutaneous, transvenous, and laparoscopic. Most often, a needle is inserted through the skin and into the liver, through which a small sample of liver tissue is extracted and sent to the lab for further testing.
Liver biopsy may be order by your doctor if you have:
- Symptoms of a liver problem, such as jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes or dark urine)
- Abnormal liver imaging or blood tests
- A chronic liver condition
How soon do results come back from a liver biopsy?
Results from a liver biopsy take a few days to come back. The liver sample goes to a pathology laboratory where the tissue is stained. Staining highlights important details within the liver tissue and helps the pathologist—a doctor who specializes in diagnosing disease—identify signs of liver disease. The pathologist looks at the tissue with a microscope and sends a report to the patient’s doctor.
How long does it take to recover from a liver biopsy?
Most patients fully recover from a liver biopsy in 1 to 2 days. Patients should avoid intense activity, exercise, or heavy lifting during this time. Soreness around the incision site may persist for about a week. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) or other pain medications that do not interfere with blood clotting may help. Patients should check with their doctor before taking any pain medications.
Possible risks and complications
- Infection
- Internal bleeding from the liver
- Damage to organs near the liver (lungs, gallbladder or intestines)
- Need for second liver biopsy if insufficient liver tissue was obtained the first time
Helpful Links

