Dysphagia is a swallowing condition in which foods or liquids do not easily pass down the esophagus, and often occurs if the esophagus walls thicken; causing a narrowing (stricture) of the passage.
Dysphagia can be caused by any of the following:
Dysphagia can be caused by any of the following: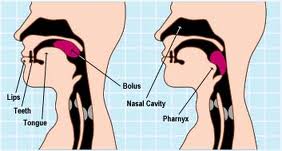
- A problem in the esophagus, such as an ulcer, stricture or cancer
- Muscles in your mouth, throat or esophagus that don’t work correctly
- A nerve or brain problem (such as a stroke) that leaves your mouth, tongue or throat muscles weak or changes how your muscles coordinate
Common Symptoms:
- Feeling chest pressure or pain when you swallow
- Choke or cough when swallowing
- Vomit after eating or drinking
- Aspirate (inhale into the lungs) foods or liquids when you swallow
- Have fatigue and weight loss
Treating Dysphagia
Your doctor may prescribe medications to neutralize or reduce stomach acids and control esophagus muscle spasms.
Esophagus dilation is a procedure that your doctor can use to widen the esophagus. It is most often done when a stricture is causing your dysphagia.
Your doctor may suggest you have an evaluation or sessions with a speck or occupational therapist. These specialists in dysphagia may give you exercises and instructions to help you eat safely.
Eating Tips:
- Eat slowly in a relaxed setting
- Don’t talk while you eat
- Sit in an upright position during and after meals
- Ask your doctor about any special diets that may help, such as liquid diets
- Thicken liquids with milk, juice, broth, gravy or starch to make swallowing easier

