What is a low FODMAP diet?
The low-FODMAP diet was developed to help manage symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other digestive concerns. FODMAPS are carbohydrates that aren’t easily absorbed in the small and large intestine and can lead to digestion issues. Symptoms like gas, abdominal pain, diarrhea and bloating are common. FODMAP’s aren’t necessarily a bad thing but bloating and diarrhea can impact your quality of life.
What does FODMAP stand for?
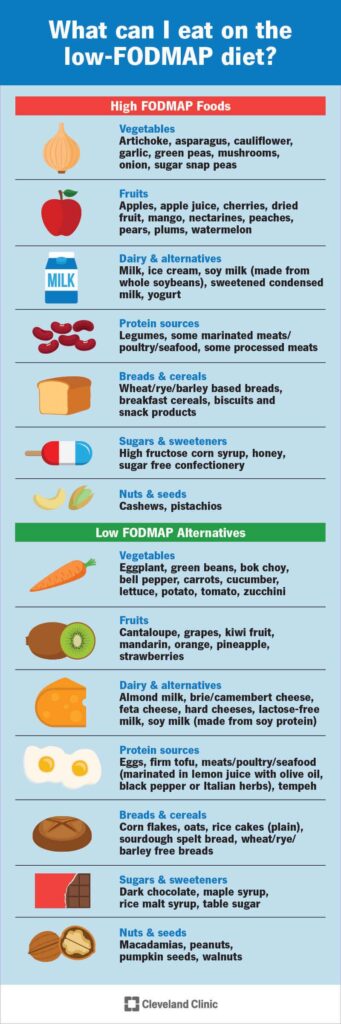
FODMAP stands for stands for Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols. Certain dairy products, fruits, vegetables, grain and sweeteners contain high amounts of FODMAP’s.
Fermentable: substances that are broken down by bacteria in your gut by a process called fermentation.
Oligosaccharides: soluble fiber known as prebiotics which feed on your gut bacteria. Examples are onion, garlic and beans.
Disaccharides: a type of carbohydrate made up of two simple sugars. The most common disaccharides are sucrose, lactose and maltose. Sucrose is commonly found in fruits, vegetables and white sugar. Lactose is found in milk and dairy products. Maltose isn’t widely found but it is in some grains and malted foods.
Monosaccharides: a simple carbohydrate and a building block of more complex carbs. The three most common monosaccharides are glucose, fructose and galactose. Glucose is found in fruits and vegetables and a primary source of energy for your body. Fructose is sugar that occurs naturally in fruits, honey and some vegetables. Galactose is derived from the breakdown of lactose so it is found in dairy products, some fruit and legumes.
Polyols: a sugar alcohol found in artificial sweeteners and naturally found in some fruits.
Who should try a low FODMAP diet?
You should always consult your physician before starting any diet. It is often prescribed for short term use for people diagnosed with IBS and SIBO. It can also be used as an elimination diet for those experiencing digestive issues to try and see what food is causing the issue. After discussing your symptoms with the physician, he or she may decide if a low FODMAP diet is right for you.
References
Cleveland Clinic. 2022. Low FODMAP Diet. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/22466-low-fodmap-diet
Food Insight. 2021. A Background on Carbohydrates and Sugars. https://foodinsight.org/background_on_carbohydrates_sugars/


