Your doctor will be able to look at each of these slices individually or perform additional visualization to view your body from different angles.
How does a CT work to diagnose gastrointestinal problems?
In some cases, CT images can be combined to create 3-D images. CT scan images can provide much more information than do plain X-rays.
At Suburban Gastroenterology, CT scans are used to diagnose and treat ailments of the liver and/or gallbladder (e.g. gallstones, abscesses, abnormal blood vessels or tumors.)
The CT test may be used to:
- Diagnose an infection
- Guide a surgeon to the right area during a biopsy
- Identify masses and tumors, including cancer
- Study blood vessels
How the Test is Performed
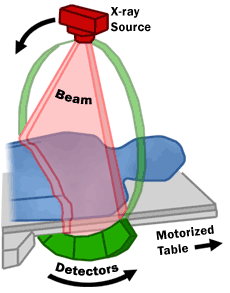
You will be asked to lie on a narrow table that slides into the center of the CT scanner.
Once you are inside the scanner, the machine’s x-ray beam rotates around you. Modern “spiral” scanners can perform the exam without stopping.
A computer creates separate images of the body area, called slices. These images can be stored, viewed on a monitor, or printed on film. Three-dimensional models of the body area can be created by stacking the slices together.
You must stay still during the exam, because movement causes blurred images. You may be told to hold your breath for short periods of time.
Complete scans usually take only a few minutes. The newest scanners can image your entire body in less than 30 seconds.
How to Prepare for a CT test
Certain exams require a special dye, called contrast, to be delivered into your body before the test starts. Contrast helps certain areas show up better on the x-rays.
Let your doctor know if you have ever had a reaction to contrast. You may need to take medicines before the test in order to avoid another reaction.
Contrast can be given several ways, and depends on the type of CT being performed.
It may be delivered through a vein (IV) in your hand or forearm.
It may be given into your rectum using an enema.
You might drink the contrast before your scan. When you drink the contrast depends on the type of exam being done. The contrast liquid may taste chalky, although some are flavored. The contrast passes out of your body through your stools.
If contrast is used, you may also be asked not to eat or drink anything for 4-6 hours before the test.
Before receiving the contrast, tell your health care provider if you take the diabetes medication metformin (Glucophage). People taking this medicine may need to stop temporarily.
Find out if the CT machine has a weight limit if you weigh more than 300 pounds. Too much weight can cause damage to the scanner.
You will need to remove jewelry and wear a hospital gown during the study
Risks of CT scans include:
- Allergic reaction to contrast dye
- Being exposed to radiation
CT scans expose you to more radiation than regular x-rays. Having many x-rays or CT scans over time may increase your risk for cancer. However, the risk from any one scan is small. You and your doctor should weigh this risk against the value of the information that will come from a CT scan.
Some people have allergies to contrast dye. Let your doctor know if you have ever had an allergic reaction to injected contrast dye.
- The most common type of contrast given into a vein contains iodine. If you have an iodine allergy, type of contrast may cause nausea or vomiting,sneezing, itching,or hives.
- If you absolutely must be given such contrast, your doctor may give you antihistamines (such as Benadryl) or steroids before the test.
- Your kidneys help remove iodine out of the body. You may need to receive extra fluids after the to help flush iodine out of the body if you have diabetes or kidney disease.
Rarely, the dye may cause a life-threatening allergic response called anaphylaxis. If you have any trouble breathing during the test, tell the scanner operator immediately. Scanners come with an intercom and speakers, so the operator can hear you at all times.
Helpful Links